Why Are Women More Likely to Experience Osteoporosis?
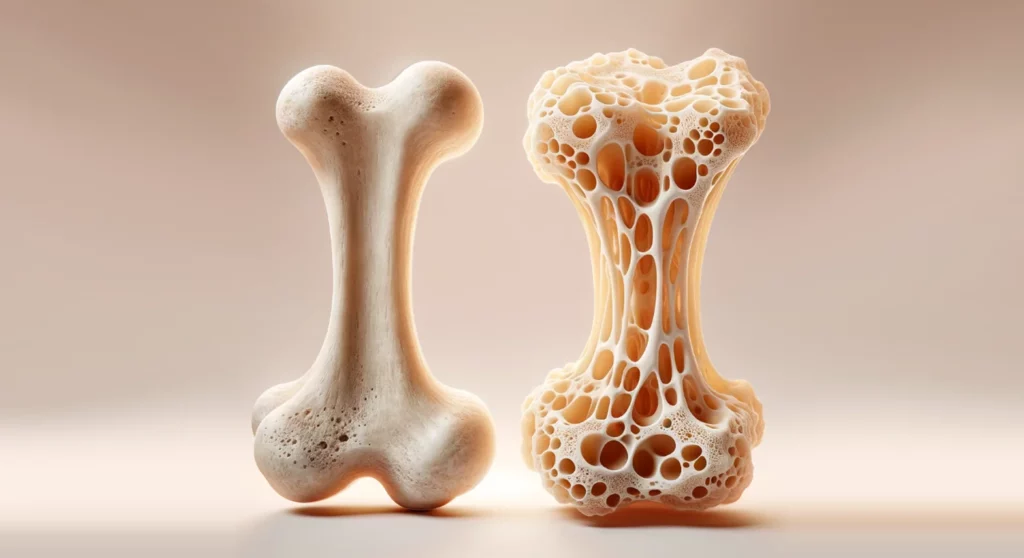
Light House Denver – Osteoporosis is a disease that causes a decrease in bone density, making bones fragile and prone to fractures. Although it can affect anyone, women are more likely to experience it than men. According to data, around 80% of people with osteoporosis are women. Why does this happen? Several biological, hormonal, and lifestyle factors explain why women are at higher risk for osteoporosis.
One of the main factors that explains why women are more susceptible to osteoporosis is hormonal changes, particularly the decrease in estrogen levels after menopause. Estrogen is a hormone that plays a vital role in maintaining bone density. When women enter menopause, the production of estrogen drastically decreases, leading to an increased loss of bone mass. Without sufficient estrogen, bones become more fragile and prone to fractures.
“Read More: Building a Healthy Marriage to Prevent Mental Health Issues”
In addition to hormonal factors, women’s body structure also plays an important role in increasing the risk of osteoporosis. Naturally, women tend to have smaller and thinner bones compared to men. Due to smaller bone size, women have less bone mass from the beginning of life. This makes them more susceptible to a decrease in bone density as they age.
Women generally live longer than men, and as they age, the risk of osteoporosis increases. In women, bone mass usually begins to decrease around the age of 30 and accelerates after menopause. In contrast, men experience a more gradual decrease in bone mass, typically starting at around 60 to 70 years old. Therefore, women are at a higher risk of developing osteoporosis at a younger age and experiencing complications from the disease.
Several lifestyle factors, such as diet, physical activity level, and smoking habits, can also influence a woman’s risk of osteoporosis. Women who do not get enough calcium or fail to engage in physical activities that support bone health, such as weight-bearing exercises, are at a higher risk of losing bone mass. Additionally, women who smoke or have a family history of osteoporosis are also more vulnerable to the disease.
Women who take certain medications, such as corticosteroids, to treat other conditions are also at a higher risk of developing osteoporosis. Long-term use of these medications can interfere with calcium absorption and accelerate bone damage.
In conclusion, osteoporosis affects women more frequently due to a combination of hormonal, structural, and lifestyle factors. Understanding these risks can help women take preventative measures to protect their bone health and reduce the likelihood of developing this debilitating condition.
“Continue Reading: Parental Behaviors That Can Lead to Bad Habits in Children”